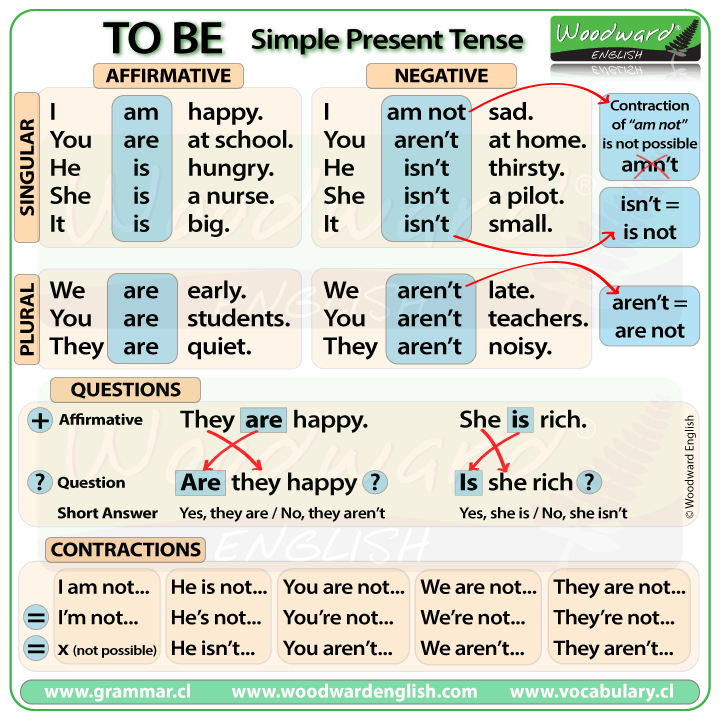
The chart
demonstrates some of the most common prepositions of place in English.
Prepositions
of Place are used to show the position or location of one thing with another.
It answers
the question "Where?"
Below we
have some more examples of Prepositions of Place:
In front of
- A band plays their music in
front of an audience.
- The teacher stands in
front of the students.
- The man standing in the
line in front of me smells bad.
- Teenagers normally squeeze
their zits in front of a mirror.
Behind
Behind is the opposite of In
front of. It means at the back (part) of something.
- When the teacher writes on the
whiteboard, the students are behind him (or her).
- Who is that person behind the
mask?
- I slowly down because there was
a police car behind me.
Between
Between normally refers to something
in the middle of two objects or things (or places).
- There are mountains between Chile
and Argentina.
- The number 5 is between the
number 4 and 6.
- There is a sea (The English
Channel) between England and France.
Across
From / Opposite
Across
from and Opposite mean
the same thing. It usually refers to something being in front of something else
BUT there is normally something between them like a street or table. It is
similar to saying that someone (or a place) is on the other side of something.
- I live across from a
supermarket (= it is on the other side of the road)
- The chess players sat opposite each other before they began their game.(= They are in front of each other and there is a table between them)
Next to
/ Beside
Next to and Beside mean
the same thing. It usually refers to a thing (or person) that is at the side of
another thing.
- At a wedding, the bride
stands next to the groom.
- Guards stand next to the
entrance of the bank.
- He walked beside me
as we went down the street.
- In this part of town there
isn't a footpath beside the road so you have to be
careful.
Near /
Close to
Near and Close to mean
the same thing. It is similar to next to / beside but there is
more of a distance between the two things.
- The receptionist is near the
front door.
- This building is near a
subway station.
- We couldn't park the car close
to the store.
- Our house is close to a
supermarket.
On
On means that something is in a
position that is physically touching, covering or attached to something.
- The clock on the
wall is slow.
- He put the food on the
table.
- I can see a spider on the
ceiling.
- We were told not to walk on the
grass.
Above /
Over
Above and Over have
a similar meaning. The both mean "at a higher position than X" but above normally
refers to being directly (vertically) above you.
- Planes normally fly above the
clouds.
- There is a ceiling above you.
- There is a halo over my
head. ;)
- We put a sun umbrella over the
table so we wouldn't get so hot.
- Our neighbors in the
apartment above us are rally noisy.
Over can also mean: physically
covering the surface of something and is often used with the word All as
in All over.
- There water all over the
floor.
- I accidentally spilled red
wine all over the new carpet.
Over is often used as a Preposition
of Movement too.
Under /
Below
Under and Below have
a similar meaning. They mean at a lower level. (Something is above it).
- Your legs are under the
table.
- Monsters live under your
bed.
- A river flows under a
bridge.
- How long can you stay under the
water?
- Miners work below the
surface of the Earth.
Sometimes
we use the word underneath instead
of under and beneath instead of below. There is no
difference in meaning those they are less common nowadays.
Under is often used as a Preposition
of Movement too.
The following is a list of prepositions in English:
- About
- Above
- Across
- After
- Against
- Along
- Alongside
- Around
- At
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beneath
- Beside
- Besides
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Despite
- Down
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Near
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Out
- Outside
- Past
- Round
- Since
- Through
- Throughout
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Underneath
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- With
- Within
- Without